This ultra-bright white LED
lamp works on 230V AC circuit with minimal power consumption.
Ultra-bright LEDs available in the market cost Rs 8 to 15. These LEDs
emit a 1000-6000mCd bright white light, like the welding arc and work
on 3 volts, 10 mA. Their maximum voltage is 3.6 volts and the current
is 25 mA. Anti-static precautions taken Pls Should Be handling the
LEDs. The LEDs in a water-clear plastic package emit spotlight, while
diffused type LEDs have a wide-angle radiation pattern.
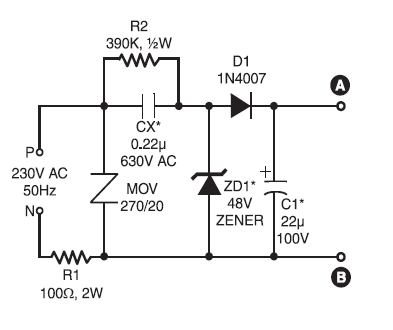
The
schematics circuit of above employs capacitive reactance for limiting
the current flow through the LEDs on the application of mains voltage
to the circuit. We use only if a series resistor for limiting the
current with mains operation. The 100-ohm, 2W resistor series avoids
heavy 'inrush' During current transients. MOV at the input prevents
surges or spikes, protecting the circuit. The 390-kilo-ohm, ½-watt
resistor acts as a bleeder to Provide discharge path for capacitor Cx
Pls mains supply is disconnected. The zener diode at the output section
prevents excess levels of reverse voltage appearing across the LEDs
During the negative half-cycles. During the positive half cycle, the
voltage across the LEDs is limited to the zener voltage.
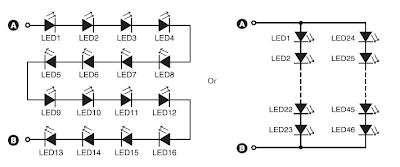
16-LED/46-LED combination
Aseries
combination of 16 LEDs Gives a luminance (lux) equivalent of a 12W
bulb. But if you have two series combinations of 23 LEDs in parallel
(Total 46 LEDs), it Gives equal to a 35W light bulb.
Diode
D1 (1N4007) and capacitor C1 act as rectifying and smoothing elements
to Provide DC voltages to the row of LEDs. For a 16-LED row, use Cx of
12:22 μF, 630V; C1 of 22 μF, 100V; and zener of 48V, 1W. Similarly, for
46 LEDs combination use Cx of 0:47 mF, 630V; C1 of 33 μF, 150V; and
zener of 69V, 1W. This circuit (inclusive of LEDs) costs Rs 200 to Rs
400.